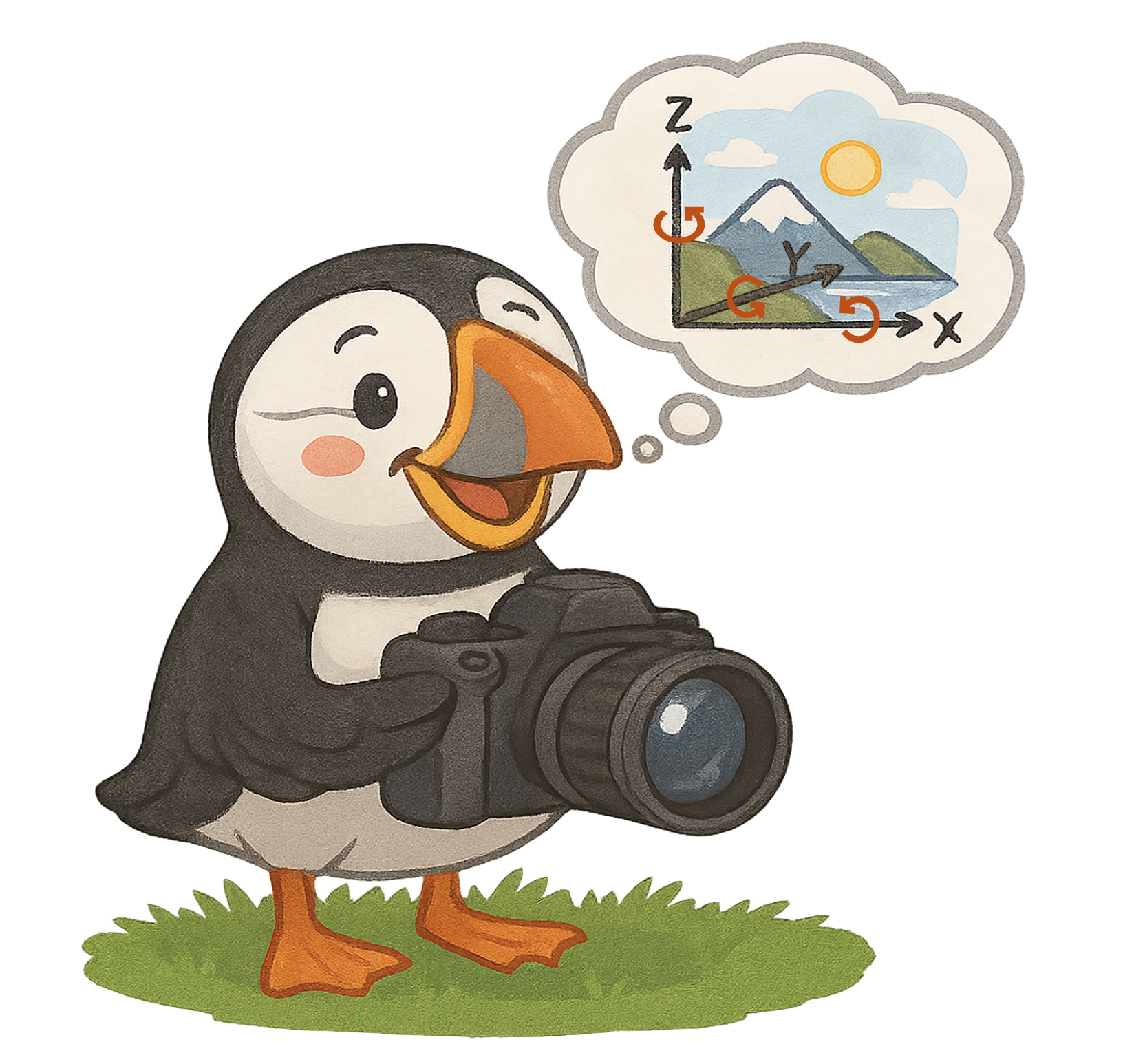
 Thinking with Camera: A Unified Multimodal Model for Camera-Centric Understanding and Generation
Thinking with Camera: A Unified Multimodal Model for Camera-Centric Understanding and Generation
Kang Liao1,
Size Wu1,
Zhonghua Wu2,
Linyi Jin3,
Chao Wang4,
Yikai Wang1,
Fei Wang2,
Wei Li1,
Chen Change Loy1
1S-Lab, Nanyang Technological University 2SenseTime Research
3University of Michigan 4Max-Planck Institute for Informatics
Arxiv 2025

Illustration of the versatile capabilities of our model. It unifies multimodal camera-centric generation (a) and understanding (b), supports the thinking mode (c), and enables diverse cross-view applications (d).
Quick Explanation
Framework
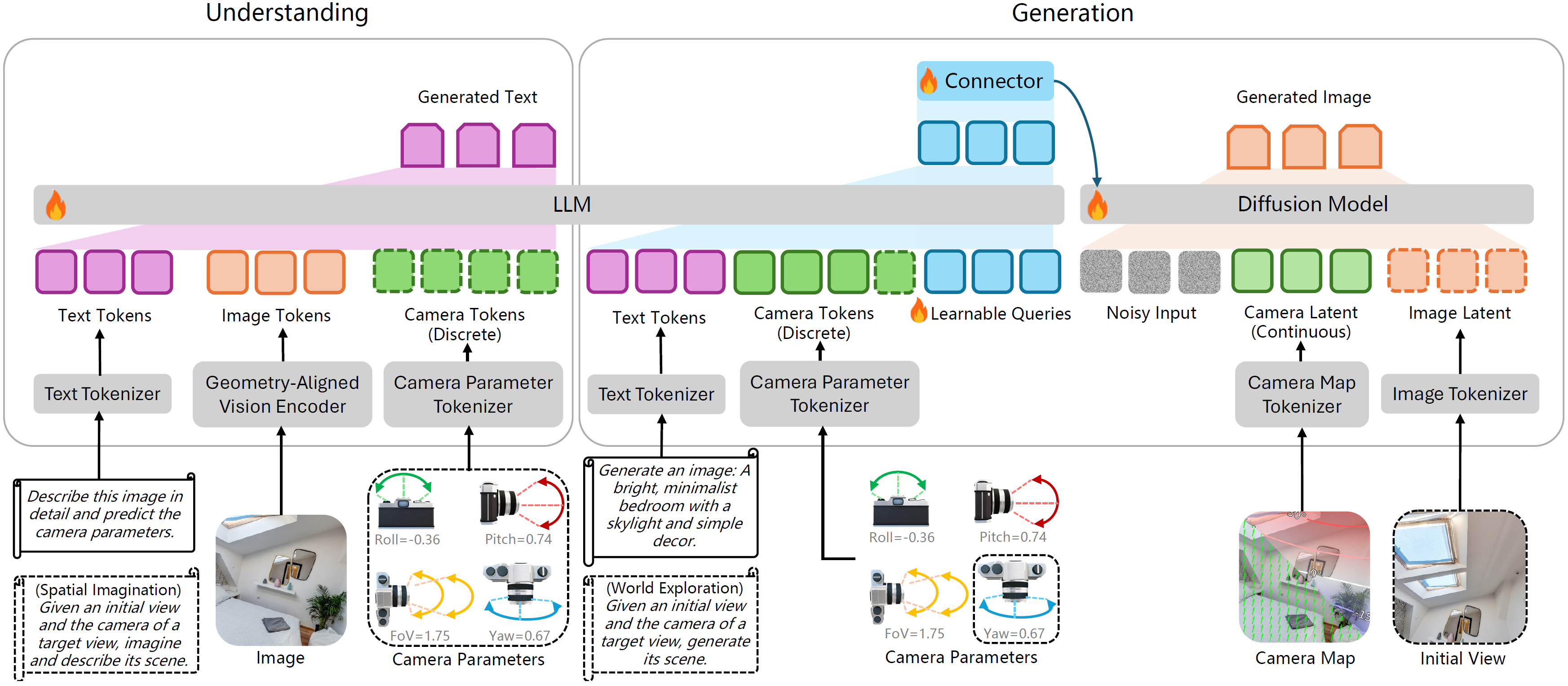
We present Puffin, a unified camera-centric multimodal model that extends spatial awareness along the camera dimension. It learns the camera-centric understanding and generation tasks in a unified multimodal framework. The elements bounded with dotted boundaries represent the cross-view understanding and generation during instruction tuning, such as spatial imagination and world exploration.
Thinking with Camera
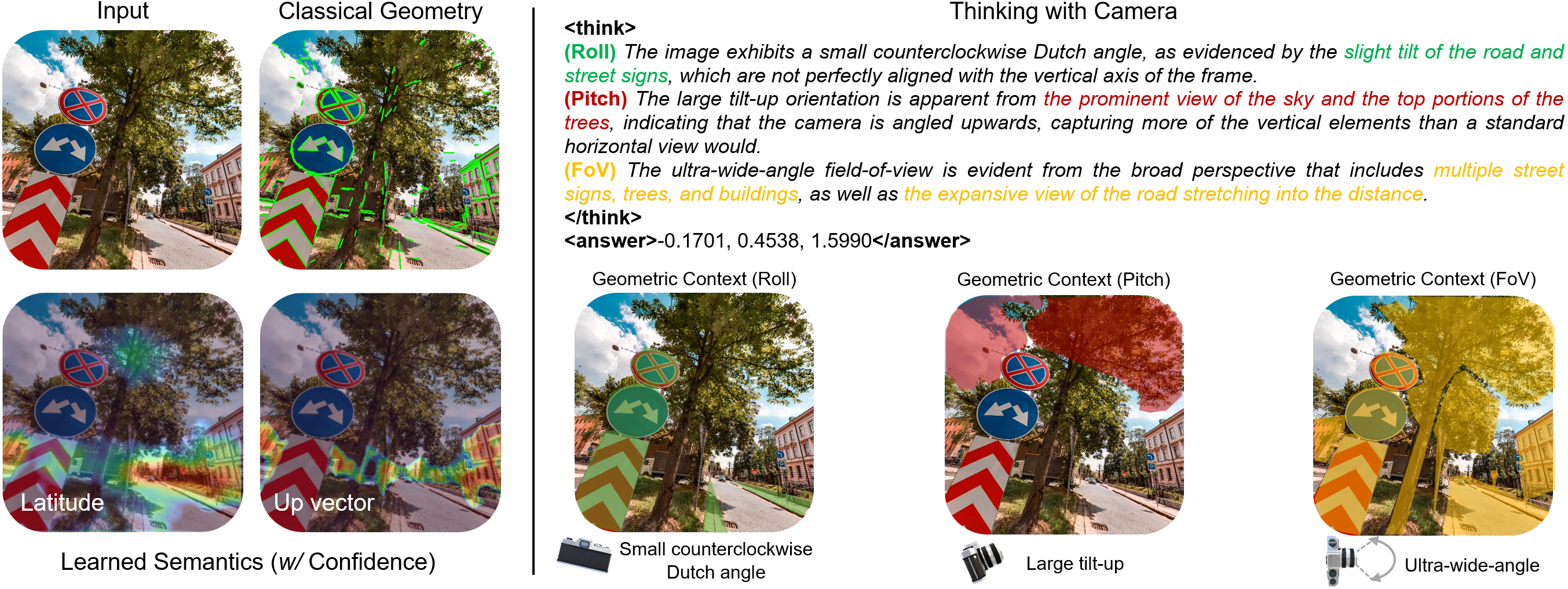
Previous methods focused on extracting or learning representations such as geometric structures or semantic features (with confidence) to estimate camera geometry from images. We introduce the notion of thinking with camera through LMMs. It decouples the camera parameters across geometric context, establishing connections between spatially grounded visual cues (highlighted in the masked regions) and professional photographic terms. The camera parameters are then predicted within the <answer></answer> tag (in radius) through this spatial reasoning process <think></think>. Please select the following samples to visualize different thinking processes.
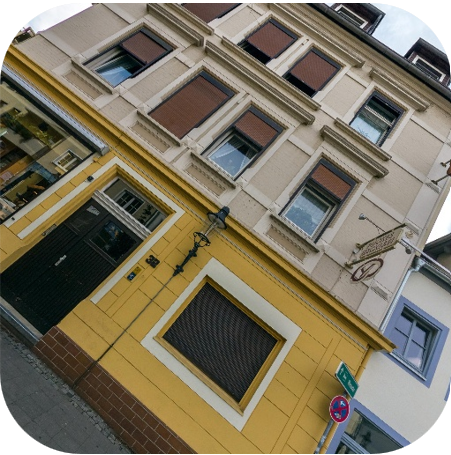
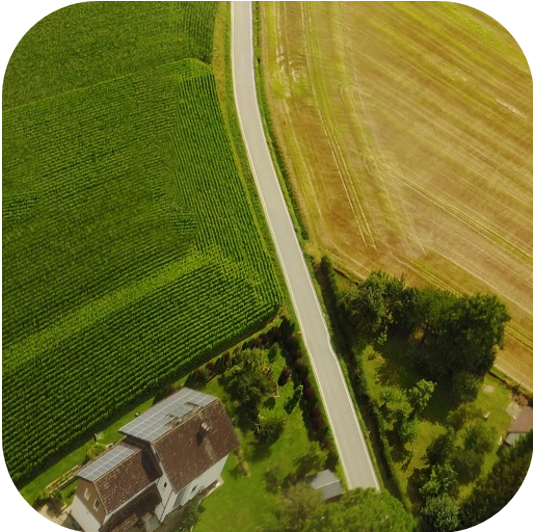
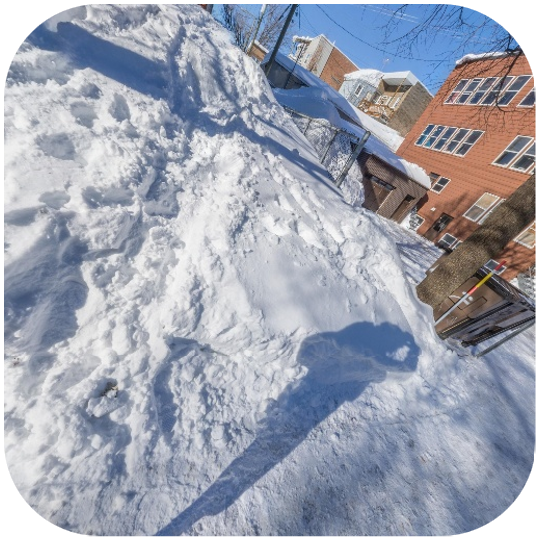





Puffin-4M Dataset
Datasets and benchmarks that span vision, language, and camera modalities remain scarce in the domain of spatial multimodal intelligence. To address this gap, we introduce Puffin-4M, a large-scale, high-quality dataset comprising 4 million vision-language-camera triplets. The pipeline of the dataset construction is illustrated as follows.
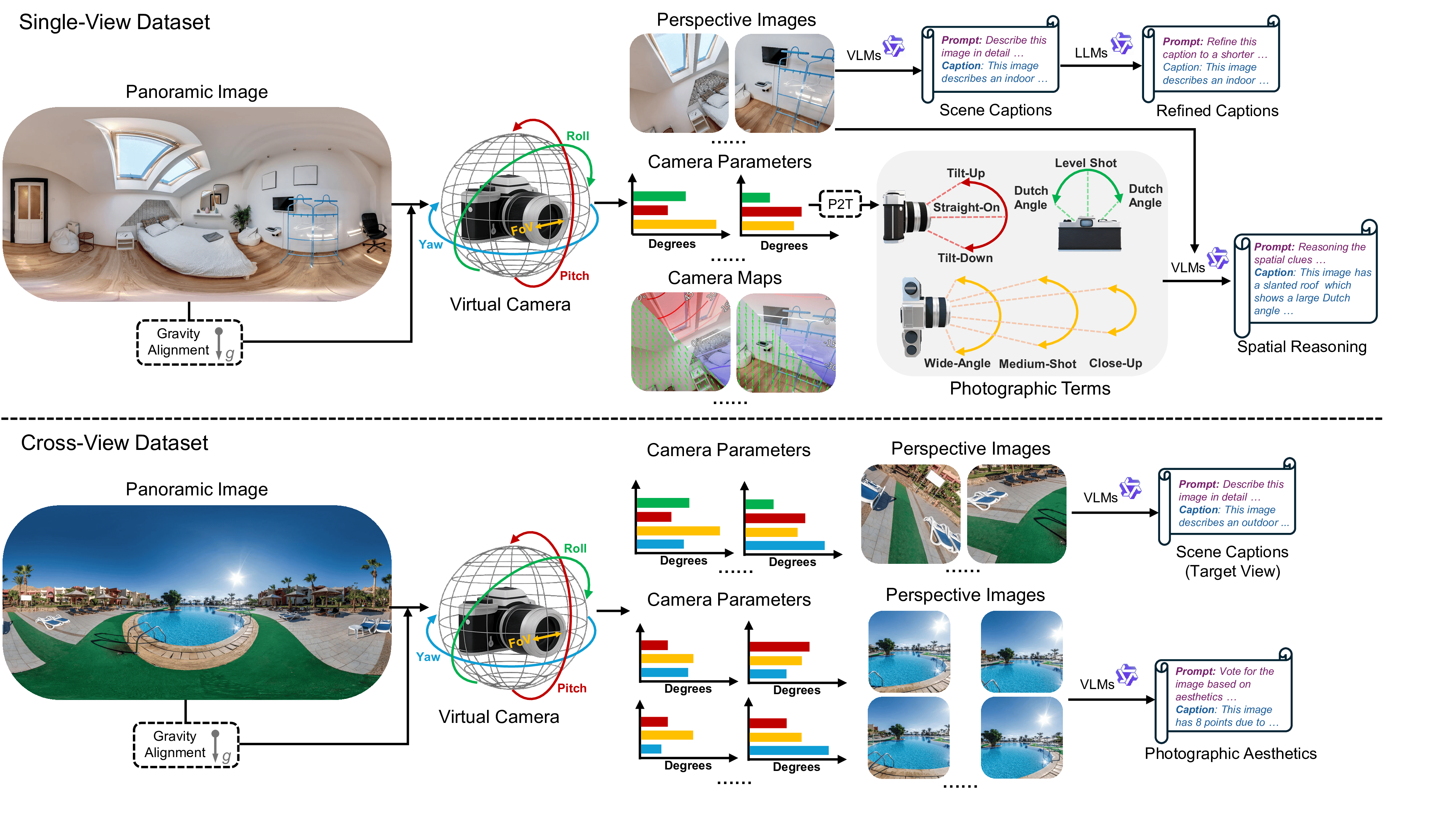
The construction of this curated dataset consists of four stages: panoramic data collection and preprocessing, perspective image generation, scene and spatial reasoning captioning, and extensions for cross-view scenarios.
Comparison Results

Qualitative comparison with the state-of-the-art camera-centric generation and understanding methods. For generated images, we adopt an offline camera calibration method to estimate their pixel-wise camera maps. We then compute the median errors of the up vector and latitude to evaluate the spatial simulation performance. For camera understanding, horizon lines are visualized from the estimated camera parameters and GT. Please refer to the Supplementary Results for more details (quantitative evaluation and more visualizations).
Applications
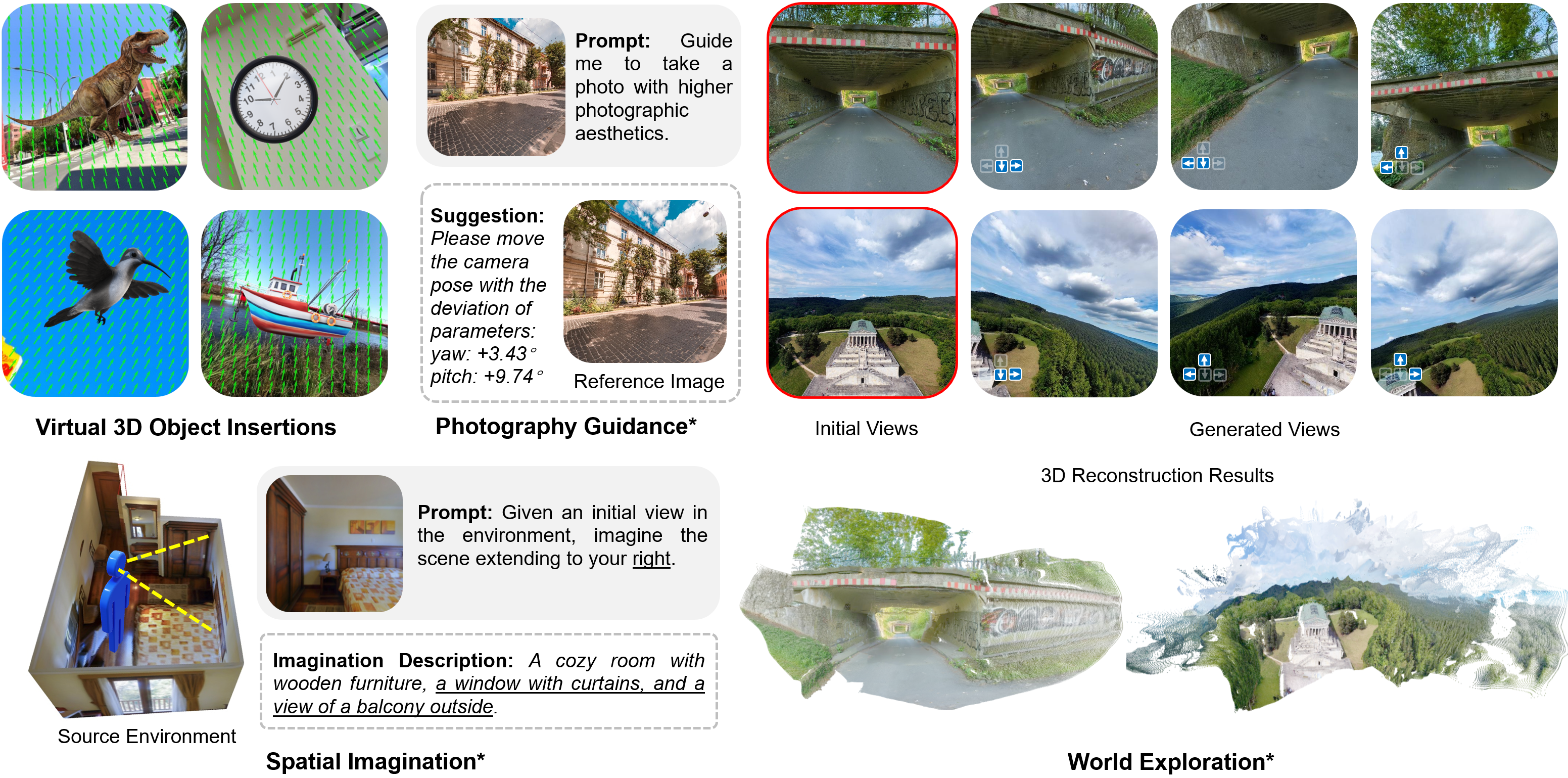
Although Puffin primarily focuses on single-view camera understanding and text-to-image camera-controllable generation, it can be flexibly extended to cross-view settings with our instruction tuning*, by appending additional tokens and switching prompts according to the target task.
 World Exploration (Cross-View Generation)
World Exploration (Cross-View Generation)
Given an initial view (marked by red box) and expected camera motion ( ), Puffin can generate the target view with proper spatial consistency. The 3D reconstructed results are derived from the initial view and generated views using VGGT.
), Puffin can generate the target view with proper spatial consistency. The 3D reconstructed results are derived from the initial view and generated views using VGGT.
By iteratively feeding the generated views into the model, Puffin can generate long-range and panorama-like scenes.
 Spatial Imagination (Cross-View Understanding)
Spatial Imagination (Cross-View Understanding)
Puffin can imagine and describe the scene of a target view given its orientation and an initial view.
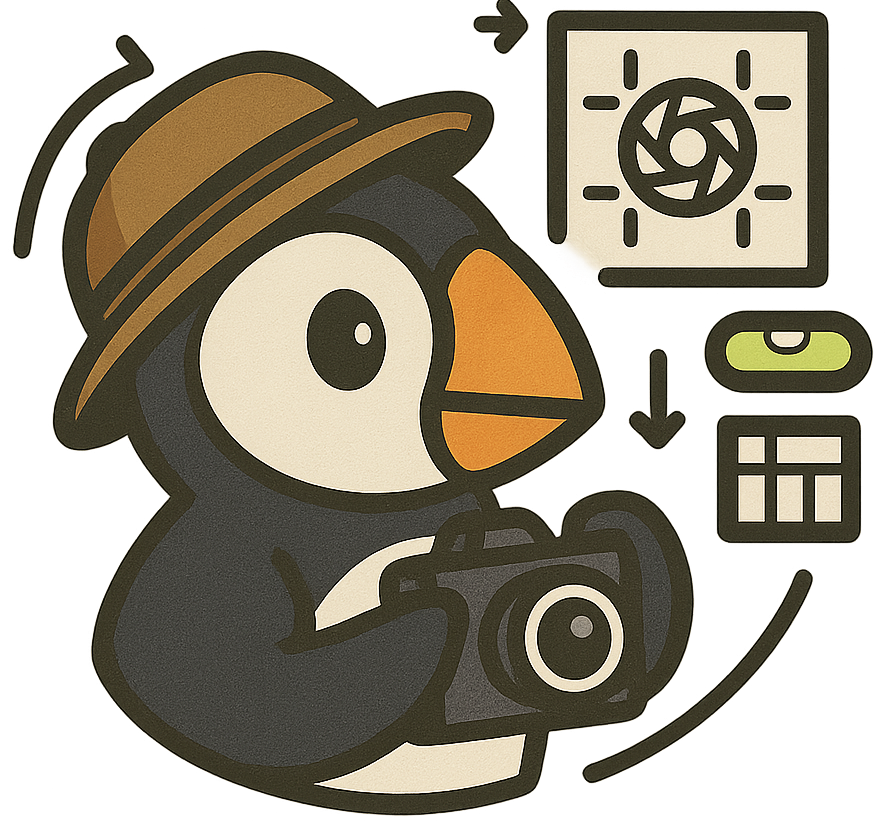 Photographic Guidance (Cross-View Understanding)
Photographic Guidance (Cross-View Understanding)
Puffin can suggest camera parameter adjustments from an initial view to achieve images with higher photographic aesthetics.
Paper

BibTeX
@article{liao2025puffin,
title={Thinking with Camera: A Unified Multimodal Model for Camera-Centric Understanding and Generation},
author={Liao, Kang and Wu, Size and Wu, Zhonghua and Jin, Linyi and Wang, Chao and Wang, Yikai and Wang, Fei and Li, Wei and Loy, Chen Change},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2510.08673},
year={2025}
}